Week 12 - Materials
4. LCA Case study - step 1
4.3. Step 4 - Interpretation
 Each LCA would be interpreted (according to ISO 14040) individually, for the incandescent lightbulb, the following interpretation was made.
Each LCA would be interpreted (according to ISO 14040) individually, for the incandescent lightbulb, the following interpretation was made.
"For the calculation of the CO2 emissions resulting from the use phase, an electricity mix of 0.55 kg CO2 per kWhEl was taken as a basis. Electricity production during use is also responsible for other environmental impact categories, but this depends very much on where the lamp is used. Equally depending on the electricity mix, the usage of an incandescent lamp may be responsible for mercury emissions. This is due to the comparatively high ratio of coal power plants in some electricity mixes, which emit mercury by burning lignite or hard coal to produce electricity". Osram, 2014
This may be followed by comparisons of similar products (such as different lightbulb types as in this case). In terms of primary energy demand, the majority of the energy was required during the user phase (98.5-99.5%) with a relatively insignificant energy requirement during manufacturing and other life cycle stages. As energy consumption was deemed to have the greatest environmental impact, this was used as a comparison. From the data below, it can be observed that the incandescent bulbs have the greatest impact due to its energy demand.
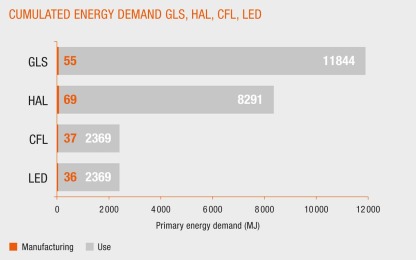
(Data courtesy of Osram, 2014)