Week 12 - Materials
1. Assessing Green Buildings
1.1. Worldwide green assessment
Most assessment systems have standard categories such as energy, water and indoor environmental quality for rating the building (Kibert, 2013). The following describes some of the assessment systems available globally.
LEED (USA)
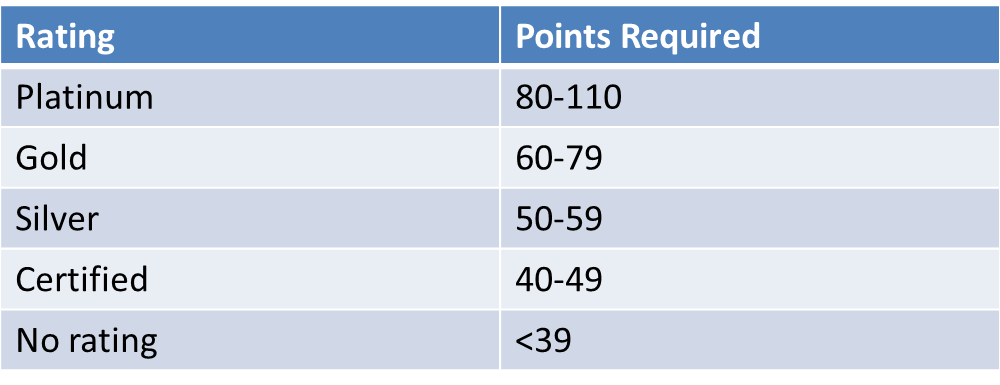
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is a product of the US Green Building Council (USGBC) and is the most frequently used building assessment in the USA. The primary objective of LEED is to determine "how green is your building?". This assessment standard provides a single number that determines the building's assessment or rating based on an accumulation of points in various impact categories. These categories include: sustainable sites, water efficiency, energy and atmosphere, materials and resources, indoor environmental quality, innovation in design and regional priority. The building is then assigned one of the following standards. There are seven minimum Program requirements (MPRs), eight parameters and a maximum of 110 points divided into 7 major categories.
The Living Building Challenge (USA)
This assessment systems was developed jointly by both the USGBC and the Canada Green Building Council and currently has >70 registered buildings pursuing certification. The Living Building Challenge is based on a few simple but very powerful concepts, among them that a building should produce as much energy as it consumes, provide all the required water, and process all its sewage. The LBC is is based on seven performance areas (or petals) and the project must meet all of the imperatives to gain adequate points for certification.
