Week 11 - Energy
Conditions d’achèvement
1. "Green" Design
1.3. Heat Transfer
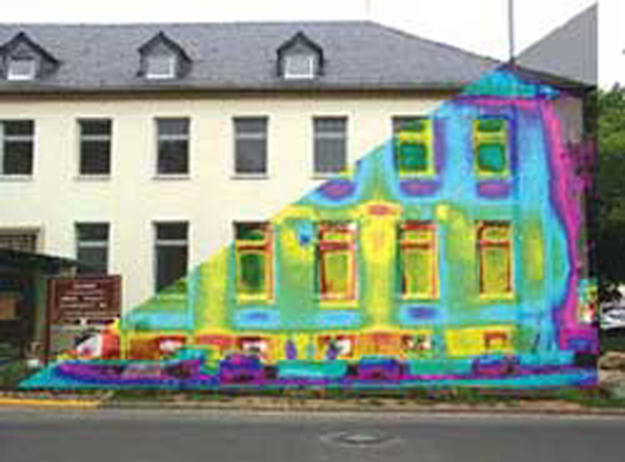 Radiation is the transfer of heat from a warmer to a cooler body and this can be reduced by the correct use of a reflective surface for example:
Radiation is the transfer of heat from a warmer to a cooler body and this can be reduced by the correct use of a reflective surface for example:
- A reflective roof to prevent solar heat gain
- Radiant barriers in small seldom used rooms (e.g attics) can reflect heat back into living spaces
- Minimising paved external areas can reduce a building's cooling load.
- Passive solar design which allows heat energy to be captured and stored by a thermal mass for later use.
(image from cnx.org)
Convection is the transfer of heat in fluid or gas and methods preventing this transfer include:
- air barriers
- Sealing gaps around windows, doors and any other openings to the exterior.
- Air-lock entrances
- Heat recovery ventilators
Conduction is the transfer of heat across a solid substance. The conductivity of a material (U-value) is the inverse of its resistance (R-value). Insulating materials have a high R-value and are important for the prevention of heat transfer by conduction. Both the amount of insulation and the benefits of insulation increase in climates which have significant temperature differences between indoor and outdoors.
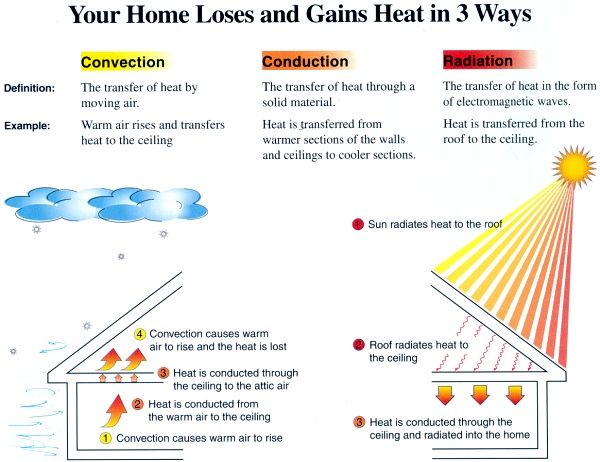
Image courtesy of houleinsulation.com