Week 11 - Energy
1. "Green" Design
1.5. Solar Heating
 Each day more solar energy falls to the Earth than the total amount of energy the planet's 5.9 billion people would consume in 27 years (National Renewable Energy Lab). However, it would be easy to be confused by the many different methods of solar heating available. Solar heating can be characterised into two main groups. Passive solar heating is the simple collection and possibly storage of solar energy. This type of design includes windows, walls and floors which are made to collect store and distribute solar energy. Whereas active solar heating includes the use of solar energy to heat water or create electricity.
Each day more solar energy falls to the Earth than the total amount of energy the planet's 5.9 billion people would consume in 27 years (National Renewable Energy Lab). However, it would be easy to be confused by the many different methods of solar heating available. Solar heating can be characterised into two main groups. Passive solar heating is the simple collection and possibly storage of solar energy. This type of design includes windows, walls and floors which are made to collect store and distribute solar energy. Whereas active solar heating includes the use of solar energy to heat water or create electricity.
Passive solar heating can be further classified into direct, indirect or isolated gain heating. Direct passive heating controls the amount of direct solar radiation reaching the living space. This may be the action of sunlight hitting a surface such as a floor or a wall. Indirect heating controls the solar radiation reaching an area of surface, such as a thermal mass, for storage and for later use. For example, this may include a thermal storage wall directly behind vertical glazing. Isolated gain refers to an attached sunspace such as a conservatory. See image below for concrete thermal mass.
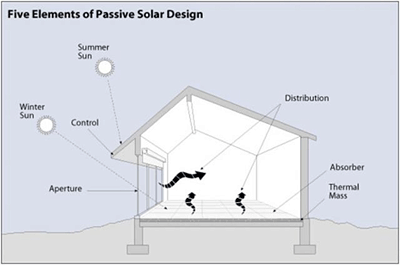
Passive solar heating contains 5 key elements:
- Collector - usually a large window of some type through which sunlight enters the building. Typically, the aperture(s) should face within 30° of true south and should not be shaded by other buildings or trees from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m. each day during the heating season.
- Absorber - a surface (usually dark in colour) to maximise heat absorption)
- Thermal Mass - usually a surface under the absorber to store the heat (see concrete area in image below) but sometimes this material can be both the absorber and the thermal mass.
- Distributor - the method by which solar heat circulates from the thermal mass to the rest of the building. May be natural convection or conduction or may be aided mechanically, e.g fans
- Controller - controls under- and overheating of a passive solar heating system, these may include roof overhangs, electronic fans switched on by temp sensors, low-emissivity blinds or awnings.